CHAPTER-8 COMPUTER NETWORKS
8.1 Evolution of Networking:
8.1.1 Introduction to Computer Networks:
Network: - To
connect the more than one devices via a medium, is called network.
1. Fast and
Secure Communication
2. Resource
sharing
3. Reduce Cost
8.1.2 Evolution of Network:
ARPANET: The
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET)
was an early packet switching network and the first network to implement the
protocol suite TCP/IP. Both technologies became the technical foundation of the
Internet.
NSFNET:
§ The National Science Foundation Network (NSFNET) was a program created
and funded by the National Science Foundation to coordinate and promote advanced research
and education in networking in the United States.
§ NSFNET was
founded in 1985. NSFNET was a general purpose research network wherein the
connection is not limited to the super computer centers, it was to serve as
a backbone connection for regional networks at every
supercomputing site and use ARPANET's TCP/IP protocol.
§ In 1986, the
super computer centers were officially connected and it became open to all
academic networks.
§ The NSF
decided to transfer the operations of NSFNET to the private sector in the midst
of the rapid growth of the network. NSFNET was officially dissolved on October
30, 1995.
Internet:
A network of networks.
WWW:
World Wide Web started on 6th August 1991, started by ‘ Berners
Lee’ .
Interspace: Interspace is a client/server software
program that allows multiple users to communicate online with real-time audio,
video and text chat in dynamic 3D environments. Interspace provides the most
advanced form of communication available on the Internet today.
8.2 Communication Terminologies:
Channel: A channel
is a separate path through which signals can flow. A channel has a certain capacity for
transmitting information, often measured by its bandwidth in Hz or its data
rate in bits per second.
Bandwidth: Bandwidth
refers to the amount of information that can be transmitted over a network in a
given amount of time, usually expressed in bits per second or bps.
Data
Transfer Rate: The data transfer rate of a computer network connection is
normally measured in units of bits per second (bps).
Larger units are Kbps,
Mbps and Gbps, KBps, MBps,GBps bps
means bit per second.
Bps means
Byte per second
1 kilobit per second (Kbps) = 1000 bits per second
(bps).
1 megabit per second (Mbps) = 1000 Kbps or 10002
bps.
1 gigabit per second (Gbps) = 1000 Mbps
1 Terabit per second (Tbps) = 1000 Gbps
8.3 Switching Techniques:
It is a way to send a message from sender to receiver.
Information may be switched as it travels through various communication
channels. There are three typical switching techniques available for digital
traffic.
•
Circuit Switching
![]()
•
Packet Switching
•
Message Switching
|
Circuit Switching |
Packet Switching |
|
Requires point to point
connections during calls. |
Sends data
in small blocks, called packets. Packets reassembled in proper sequence at
the receiver end. |
|
Required dedicated connection |
Not
required dedicated connection |
|
Circuit-switched networks were
used for phone calls |
packet-switched
networks handled data |
8.4 Transmission Medium:
A medium which is used to connect the devices and transfers the
data from one device to another device.
8.5 Network Devices:
1. Modem
2. Hub
3. Switch
4. Gateway
5. Bridge
6. Router
7. Repeater
8. NIC (Network
Interface Card)
9. RJ45
Connector
1. Modem:
Ø The full
form of modem is Modulator and demodulator.
Ø A modem is a
device or program that enables a computer to transmit data over telephone or
cable lines.
Ø A modem
converts analog signal to digital signal and vice- versa.
Ø Modem
connects computer to internet.
Ø There are
two types of modem:
a. Internal Modem
b. External Modem
Fig. : Working of Modem
2. Hub:
• A network
device that contains multiple ports.
• Provides
multiple connections.
• When a packet arrives at one port, it
is copied to the other ports so that all segments of the LAN can see all
packets.
• Two types of
hub :
a. Active Hub
Fig: Hub Fig. : Active and Passive Hub
3.
Switch:
• A switch is
called smart hub.
• Provides
multiple connections
• A device
that filters and forwards packets between LAN
segments.
Fig:
Switch
|
HUB
|
SWITCH |
|
Hub passes
the frame to every port. |
Passes the frame to a specific
port, because it keeps a record of MAC address. |
|
Creates
lot of traffic on network |
Less
traffic |
|
Hub shares its bandwidth with each
and every port, so bandwidth divided among all the nodes, which will degrade
performance. |
Switch
allocates full bandwidth to each of its port. So user always access maximum
amount of bandwidth. |
|
Slow speed
|
Fast speed
|
4.
Gateway:
A gateway is
a network point that acts as an entrance to another network. Used to
connect two dissimilar networks.
5.
Bridge:
A device that connects two local-area networks (LANs), or
two segments of the same LAN that use the same protocol, such as Ethernet.
6.
Router:
• A router is
a device that forwards data packets along networks. A router is connected to at
least two networks, commonly two LANs or WANs. Routers are located at gateways,
the places where two or more networks connect.
• A router
acts as a dispatcher, choosing the best path for information to travel so it’s
received quickly.
7.
Repeater:
Network repeaters regenerate and amplify the weak signals to
transmit the information for long distance.
8.
NIC (Network
Interface Card): NIC card has a physical address of a system; this physical
address known as MAC address.
A MAC address is
a 6- byte address with each byte separated by a colon. First 3-bytes have
Manufacturer id and last 3-bytes represent Card id. 10:BE:05:56:3F:CB
![]()
9. RJ45 Connector: It is used for connecting computers onto Ethernet-based local area networks (LAN). RJ stands for Registered Jack. It is a standardize networking interface. 45 is the number of the interface standard. It has 8-pins.
8.6 Types of Network:
1. Local Area
Network (LAN)
2. Metropolitan
Area Network (MAN)
3. Wide Area
Network (WAN)
4. Personal
Area Network (PAN)
![]()
1. LAN:
*Use in small local area, like in an institute or an
organization.
* Devices are
connected via physical medium.
* Limited
distance, up to 150 Meter.
* Example – Intranet
2. MAN:
* Larger than
LAN.
* Used in
Metropolitan cities. *Range up to 50 KM.
3. WAN:
* Large
network
* Public
* Example – Internet
4. PAN:
*
For very small distance
*
Private Communication
*
Example: Bluetooth
8.7
Network Topology:
The term Topology
refers to the way/layout in which the various nodes or computers of a network
are linked together.
The
following factors are considered while selecting a topology:
ü Cost
ü Reliability
ü Bandwidth
capacity
ü Ease of
installation
ü Ease of
troubleshooting
ü Delay
involved in routing information from one node to another.
![]()
8.7.1
Types of Topologies
1.
Bus Topology
It consists of one continuous length of cable (trunk) that
is shared by all the nodes in the network and a terminating resistor
(terminator) at each end that absorbs the signal when it reaches the end of
line. Without a terminator the electrical signal would reach the end of copper
wire and bounce back, causing errors on the network.
Data communication message travels along the bus in both
directions until it is picked up by a workstation or server NIC. If the message
is missed or not recognized, it reaches the end of the cabling and dissipates
at the terminator. Bus Network Topology requires a multipoint connection.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
1.
Easy to install and the use for small networks. 2.
Requires less cable 3.
Failure of one node does not affect the network
functioning. 4.
Cost is less 5.
New node can be easily added |
1.
If the main cable fails the entire network collapses. 2.
Difficult to reconfigure, due to more connections. 3.
Difficult to troubleshoot 4.
Slow, due to traffic on
single cable 5.
Only one device transmits at a time, other devices wait
for their turn. |
2. Ring Topology
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages
|
|
1.
Easy to troubleshoot
2.
There is no master computer on controller. 3.
There are no collisions. 4.
Fast speed 5. Easy
fault detection and isolation |
1.
Requires more cable 2.
More Expensive 3.
A break in cable ring brings down entire network 4.
Data flows in single direction |
The physical
ring Topology is a circular loop of point-topoint links. Message travel around
the ring from node to node in a very organized manner. Each workstation checks
the message for a matching destination address. If the address doesn’t match
the node simply regenerates the message and sends it on its way. If the address
matches, the node accepts the message and sends a reply to the originating
sender.
3. Star Topology
The physical
star Topology uses a central controlling hub with dedicated legs pointing in
all directions – like points of a star. Each network device has a dedicated
point-to-point link to the central hub. There is no direct link between these
computers and the computers can communicate via central controller only.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
1.
Easier to add new node or modify any existing node without
disturbing network. 2.
Fast Speed 3.
If any local computer or link fails, the entire system
does not collapse 4.
Easy fault detection and isolation 5.
Central node control |
1.
Central node dependency. If the central controller or hub
fails, entire system collapses. 2.
Cabling cost is more 3.
Difficult to install |
4. Mesh Topology
![]() In mesh
topology, each node is connected to every other node in the network i.e. each
node has a dedicated point to point link to every other node as shown.
Dedicated means that the link carries the traffic only between two devices it
connects.
In mesh
topology, each node is connected to every other node in the network i.e. each
node has a dedicated point to point link to every other node as shown.
Dedicated means that the link carries the traffic only between two devices it
connects.
In this way there
exist multiple paths between two nodes of the network. In case of failure of
one path, the other one can be used.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
1.
It is robust. Failure of one node does not collapse the
entire system. 2.
No traffic congestion 3.
Dedicated links ensure faster transmission 4.
Point to point links makes fault identification and
isolation easier. |
1.
Network installation and reconfiguration difficult. 2.
High cabling cost. If there are n nodes in the network
then each node has (n-1) connections. |
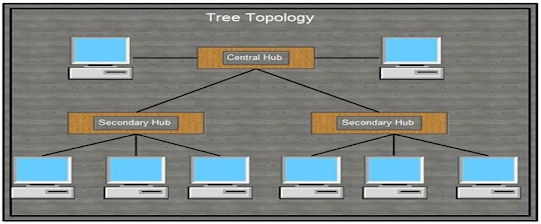
5. Tree Topology
This topology has Hierarchical structure. This topology
connects the node via hubs. Hub, which is present at top level, is called root hub or active hub. Another hub is called secondary hub or passive hub.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
1. New
node can be added easily. 2. Signal
can travel for long distance. 3.
Isolate and prioritize communication. |
1. If
the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down. 2. More
difficult to configure 3.
Higher cabling cost
|
|
|
|
6. Hybrid Topology:
It is a composition of more than one topology.
8.8 Network Protocol:
1.
TCP:
Transmission Control Protocol – 4 layers
|
Application
Layer |
|
Transport
Layer |
|
Internet
|
|
Network
Interface |
2.
IP:
Internet Protocol
Each computer has unique address over
internet, is called IP address. An IP
address is an identifier for a computer or device on a TCP/IP network.
![]()
Two
types:
I.
IPv4 (32-bits or 4-bytes) : IPv4 addresses are
canonically represented in dotdecimal notation, which consists of four decimal
numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255, separated by dots, e.g., 192.168.1.1.
II.
IPv6 (128-bits or 16-bytes)
3.
FTP
(File Transfer Protocol): use to transfer files from one computer to another
computer.
4.
PPP
(Point to Point Protocol)
5.
HTTP(
HyperText Transfer Protocol): To transfer the hypertext pages over internet.
6.
Telnet
(TELecommunication NETwork) : A network protocol that allows a user on one
computer to log into another computer(remote) that is part of the same network
or on the internet.
7.
GSM:
GSM (Global System for Mobile
communication) is a digital mobile telephony system that digitizes and
compresses data, then sends it down a channel with two other streams of user
data, each in its own time slot.
8.
CDMA: Code
Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
is a digital air interface standard, claiming eight to fifteen times the
capacity of traditional analog cellular systems.
Each user is separated
by a unique code; all users can
share the same frequency band.
CDMA is a
spread spectrum technology, which means that it spreads the information
contained in a particular signal of interest over a much greater bandwidth than
the original signal.
9.
GPRS: General Packet Radio Service is a
packet-switching technology that enables data transfers through cellular
networks (wireless). It is used for mobile internet, MMS and other data
communications. In theory the speed limit of GPRS is 115 kbps, but in most
networks it is around 35 kbps.
10.
WLL:
Wireless Local Loop is a system that connects
subscribers to the local telephone station wirelessly.
Fig.
: Architecture of WLL
FSU : Fixed Subscriber
Unit BSC : Base Station
Controller BTS: Base
Transceiver Station
11.
VoIP
: VoIP (voice over IP) is the transmission of voice and multimedia content over
Internet Protocol (IP) networks. This protocol is used for chat and video
conferencing over internet.
8.9
Mobile Telecommunication Technologies:
Firstly, when wireless generation started, it
was analog communication. That generation is 1G. They used various analog
modulation for data transfer. Now when the communication migrated from analog
to digital, the foundation of latest communication were led. Hence came 2G.
1G Technology:
• 1G
refers to the first generation of wireless telephone technology, mobile
telecommunications which was first introduced in 1980s and completed in early
1990s. It’s Speed was upto
2.4kbps, allowed the voice calls in one country.
• It
used Analog Signal and AMPS was first launched in USA in 1G mobile systems
• Poor
Voice Quality
• Poor
Battery Life
• Large
Phone Size
• No
Security
• Limited
Capacity
• Poor
Handoff Reliability
2G
Technology:
• 2G
technology refers to the 2nd generation which is based on GSM. It was launched in
Finland in the year 1991 and used digital signals.
• It’s
data speed was upto 64kbps.
Features
include:
• It
enables services such as text messages, picture messages and MMS (multi media
message).
• It
provides better quality and capacity.
Drawbacks:
• 2G
requires strong digital signals to help mobile phones work. If there is no
network coverage in any specific area, digital signals would weak.
• These
systems are unable to handle complex data such as Videos.
![]() 3G
Technology:
3G
Technology:
• 3G
technology refer to third generation which was introduced in year 2000s.
• Data
Transmission speed increased from 144kbps- 2Mbps.
• Typically
called Smart Phones and features increased its bandwidth and data transfer
rates to accommodate web-based applications and audio and video files.
Features Include:
• Providing
Faster Communication
• Send/Receive
Large Email Messages
• High
Speed Web / More Security
• Video
Conferencing / 3D Gaming
• TV
Streaming/ Mobile TV/ Phone Calls
• Large
Capacities and Broadband Capabilities
• 11
sec – 1.5 min. time to download a 3 min Mp3 song.
Drawbacks:
• Expensive
fees for 3G Licenses Services
• It
was challenge to build the infrastructure for 3G High
Bandwidth Requirement Expensive 3G Phones.
• Large
Cell Phones
4G Technology:
• 4G
technology refer to or short name of fourth Generation which was started from
late 2000s.
• Capable
of providing 100Mbps – 1Gbps speed.
• One
of the basic term used to describe 4G is MAGIC.
Features Include:
• Mobile
Multimedia
• Global
Mobility Support
• Integrated
Wireless Solution
• Customized
Personal Services
• Also
known as Mobile Broadband Everywhere
• The
next generations of wireless technology that promises higher data rates and
expanded multimedia services.
• Capable
to provide speed 100Mbps-1Gbps.
• High
QOS and High Security
• Provide
any kind of service at any time as per user requirements, anywhere.
• More
Security
• High
Speed
• High
Capacity
• Low
Cost Per-bit
Drawbacks:
• Battery
uses is more
• Hard
to implement
• Need
complicated hardware
• Expensive
equipment required to implement next generation network.
5G
Technology: Introduced in 2020
o Faster
than 4G.
o Gateway
for Internet of Things (IoT) o More secure than 4G
o Un-interrupted
and Reliable o Less latency than 4G. o Less
interference and better efficiency o Cloud
based computing
The basic difference between 3G, 4G and 5G is
in data transfer and signal quality.
|
Technology |
3G |
4G |
5G |
|
Data Transfer Rate |
3.1 MB/sec |
100 MB/sec |
>1Gbps |
|
Internet Services |
Broadband |
High Broadband |
Ultra Broadband |
|
Mobile – TV Resolution |
Low |
High |
Very High |
|
Frequency |
1.6-2 GHz |
2-8 GHz |
25 GHz |
|
Download and upload |
5.8 Mbps |
14 Mbps |
200-400 Mbps |
|
Latency |
100-500 milliseconds |
20-30
milliseconds |
< 10 milliseconds |
8.10 Introduction to web services:
8.10.1
WWW:
World Wide Web is an information system where websites and
webpages are interconnected and
accessible through URL. It is also known as Web.
8.10.2
HTML: HTML is the standard
markup language for creating Web pages.
• HTML
stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
• HTML
describes the structure and design of Web pages using markup
• HTML
elements are represented by tags
• Browsers
do not display the HTML tags, but use them to render the content of the page The
current version of HTML is HTML 5.0
A simple HTML Code: OUTPUT
8.10.3 XML :
• XML stands
for EXtensible Markup Language
• XML is a
markup language much like HTML
• XML was
designed to store and transport data
• XML was
designed to be self-descriptive XML is a W3C Recommendation
|
S. No.
|
HTML |
XML |
||||||
|
1
|
HyperText
Markup Language.
|
eXtensible
Markup Language.
|
||||||
|
2
|
Designed to display data with
focus on how data looks. |
XML was designed to be a software
and hardware independent tool used to transport and store data, with focus on
what data is. |
||||||
|
3
|
|
HTML is case insensitive. |
|
|
XML is case sensitive. |
|
||
|
4
|
HTML is used for designing a
web-page to be rendered on the client side. |
XML is used basically to transport
data between the application and the database. |
||||||
|
5
|
HTML has its
own predefined tags.
|
Uses custom
tags defined by the user.
|
||||||
|
6
|
HTML
is not strict if the user does not use the closing tags. |
XML makes it mandatory for the
user the close each tag that has been used. |
||||||
|
7
|
|
HTML does not preserve white
space. |
|
|
XML preserves white space. |
|
||
|
8
|
HTML is about displaying data,
hence static. |
XML is about carrying information
hence dynamic. |
||||||
8.10.4 Domain Name:
Domain names are used to identify one or more IP addresses. Domain names are used in
URLs to identify particular web page.
For
example, http://www.kvongcbrd.com/english-results.htm

Every domain name has a suffix that indicates which top
level domain (TLD) it belongs to. There are only a limited number of such
domains. For example:
§ gov - Government agencies
§ edu - Educational institutions
§ org - Organizations (nonprofit)
§ mil - Military
§ com - commercial business
§ net - Network organizations
§ in - India
§ th – Thailand
Because the Internet is based on IP addresses, not domain
names, every Web server require a Domain Name System (DNS) server to translate
domain names into IP addresses.
8.10.5 URL: Uniform Resource Locator. It is the global address of documents and
other resources on the World Wide Web.
8.10.6 Website: Collection of web pages which are
interlinked to one another. These pages are hypertext pages and link between
pages is known as hyperlink.
8.10.7 Web browser: It is application software though
which user can access internet. Example: internet explorer, Google chrome,
Mozilla Firefox, opera, UC browser
8.10.8 Web Server: A web server is a system that uses
HTTP to accept request and serve the web pages as response to users. Every web
server has IP address.
Example: Apache web server, Microsoft's
Internet Information Server
(IIS) and nginx (pronounced engine
X) from NGNIX.
8.10.9 Web Hosting:
o
Web hosting is a service that allows organizations and
individuals to post a website on to the Internet.
o
A web host, or web hosting service provider, is a business
that provides the technologies and services needed for the website or webpage
to be viewed in the Internet.



























Post a Comment